Safe and Accurate Metal Cutting Techniques
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Metal Cutting Methods
- Essential Safety Measures
- Choosing the Right Tools
- Maintaining Cutting Equipment
- Best Practices for Precision Cutting
- Training and Certification
- Emerging Technologies in Metal Cutting
- Conclusion
Metal cutting stands as a cornerstone process across industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and construction. Mastering both safety and precision not only preserves the quality of finished products but also safeguards the workforce. Leveraging the right precision metal cutting technique is critical, as each cut impacts the structural integrity and performance of the final output. This detailed guide explores actionable methods, advanced tools, and best practices to achieve safe and accurate metal cutting results every time. This article emphasizes the importance of a tailored approach to metal cutting applications, highlighting the need for operational safety and precise cutting accuracy. It emphasizes the need to avoid errors, material waste, and workplace accidents, highlighting the need for better outcomes.
Understanding Metal Cutting Methods
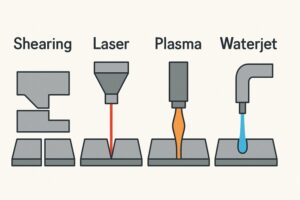
Metal cutting methods vary based on material type, thickness, and specifications. Four primary techniques dominate the industry: shearing, laser cutting, plasma cutting, and waterjet cutting. Shearing is a mechanical technique used for simple cuts in sheet metal, while laser cutting is ideal for delicate or small-scale designs. Plasma cutting uses high-velocity jets of ionized gas to slice through conductive metals, while waterjet cutting uses high-pressure water streams to carve through metal without heat. Selecting the correct method ensures each part’s strength, finish, and dimensional accuracy, reducing wasted material and rework.
Essential Safety Measures
Metalworking operations require strict safety protocols to prevent injuries and project delays. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as glasses, gloves, ear protection, and flame-resistant clothing is essential for safeguarding staff and output. Work areas should be clean and organized, with flammable materials removed, lighting provided, and clamps used to secure workpieces. Equipment inspections should be conducted before any project to check for wear, debris, and functional safety guards. These measures significantly reduce accident risks and promote a productive workflow.
Choosing the Right Tools
The choice of tools significantly influences the precision and quality of a metal cutting job. Key factors include material compatibility, tool condition, and ergonomics. For instance, a heavy-duty plasma cutter is ideal for thick steel, while a laser is ideal for thin, intricate materials. It’s crucial to ensure the tools are sharp and in top working order before each use to prevent ragged edges and stall operations. The right tools streamline workflow and reduce operator errors and equipment downtime.
Maintaining Cutting Equipment
Regular maintenance of equipment extends its life and maintains cutting quality. Best practices include cleaning machines after use, lubricating moving parts, and sharpening blades and bits. Regular calibration is crucial for machines like CNC and laser cutters, ensuring consistent, reliable results. Attention to machine maintenance ensures every job meets high accuracy and safety standards.
Best Practices for Precision Cutting
Focus on expert technique and equipment to achieve sharp, dimensionally correct cuts. Double-check measurements and mark cut lines clearly to avoid mistakes. Maintain a stable stance, grip tools firmly, and follow guidelines without rushing. Use machines at their recommended speeds to avoid overheating, blade wear, or warping the metal. These practices make repeatable, high-quality cuts a standard procedure on any project site.
Training and Certification
Untrained operators pose a significant risk to themselves and others. Proper training and certification are crucial in high-stakes metal cutting environments. Training ensures proper equipment usage and safety protocols, while certifications validate competency and demonstrate consistent high standards. Continuous education keeps staff skilled in new techniques and technologies. Investing in workforce training meets legal requirements and drives operational success.
Emerging Technologies in Metal Cutting
The advancement of technology is revolutionizing the metal cutting industry, enhancing efficiency and precision. Automated equipment manages repetitive cuts with minimal supervision, improving worker safety. AI-integrated machinery optimizes cutting paths in real-time, reducing downtime and material waste. Advanced materials, such as more resilient cutting blades and tool coatings, prolong tool life and improve speed and quality. Adopting innovative tools and techniques provides a competitive advantage, enabling higher throughput, better safety, and unmatched precision.
Conclusion
Excellence in metal cutting is defined by the careful combination of modern technologies, rigorous safety protocols, and professional know-how. Organizations can achieve safe, precise, and productive metal cutting operations by understanding the primary methods, enforcing strict safety measures, choosing and caring for the right tools, adopting best practices, and prioritizing ongoing training. Staying current with emerging innovations ensures that your approach to metal fabrication remains both effective and ahead of the curve.

